Injection molding is all around us. It’s a key processus de fabrication. Thousands of plastic parts come to life by shooting hot material into a mold. It’s big for making lots of products fast. You’ll find parts made this way in cars, medical devices, toys, and electronics. It’s perfect for making complex shapes on a large scale.
The Society of Manufacturing Engineers plays it up big time. So does the American Injection Molding Institute with their learning programs. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) checks out the new perks and better ways to do things in this area.
Principaux enseignements
- Injection molding fires up massive production of plastic parts.
- Le présent processus de fabrication supports big fields like automotive, healthcare, and electronics.
- It’s a whiz at making complicated shapes with great detail.
- Groups like The Society of Manufacturing Engineers and NIST share cool updates.
- The American Injection Molding Institute’s courses teach the ins and outs of techniques de moulage des matières plastiques.
Introduction au moulage par injection
Injection molding plays a key role in today’s manufacturing world. It’s known for its efficiency and precise outcomes. To understand it better, we’ll look into what it is, its history, and its wide use in different sectors.
Definition and Background
Le terme plastic injection molding definition refers to a process where hot material fills a mold, then cools and hardens into a new shape. It began in the late 1800s and has come a long way since then. Innovators like John Wesley Hyatt were crucial in history of molding’s development. Now, the technique is used with various materials including metals and glass, not just plastics.
Applications dans diverses industries
Injection molding is versatile, benefiting many industries. In automotive, it makes detailed parts like car dashboards and bumpers very accurately. The aerospace sector uses it for strong, light components.
Consumer electronics also gain from this method for making complex items, such as smartphone cases. In healthcare, it’s critical for producing everything from syringes to complex tools for surgery. Research in The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology highlights this process’s crucial role in these fields.
Le processus de moulage par injection
Injection molding turns raw material into products through detailed steps. Each phase is key for quality and efficiency.
Step-by-Step Breakdown
Here are the main stages of injection molding:
- Serrage : The mold’s two halves are closed tightly. This ensures no material leaks during injection.
- Injection : Molten polymer is shot into the mold. Being precise here is crucial for the best outcome.
- Refroidissement : The material then cools and firms up inside the mold. This step affects how long the process takes.
- Ejection : After cooling, the part is removed from the mold. It’s then ready for further steps or assembly.
Common Techniques and Variations
Different techniques make injection molding better:
- Overmolding: This method molds one material over another to create a single item.
- Insert Molding: Puts a pre-made piece inside the mold so plastic surrounds it.
- Gas-Assisted Injection Molding: Gas helps fill the mold, using less material and time.
Delving into injection molding shows how crucial process optimization is. Companies like Engel and Husky lead the way. They focus on less waste, quicker cycles, and top-notch quality.
How Does Injection Molding Work?
Injection molding uses the rules of thermodynamics and fluid dynamics. It needs exact temperature control for consistent, quality parts. The process makes plastic by heating and molding it carefully.
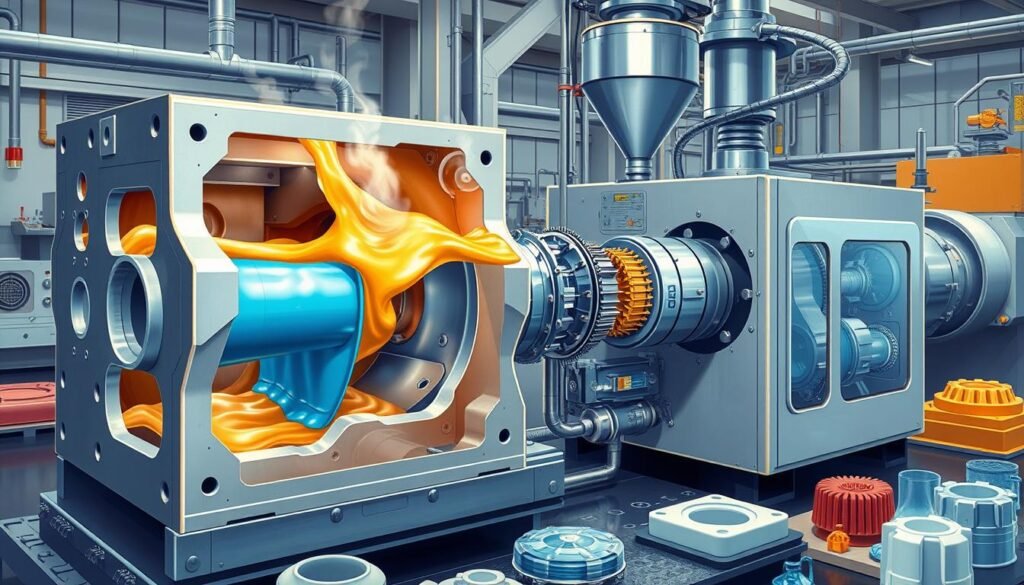

The Science Behind the Process
To grasp injection molding, knowing the science is key for those making industrial plastic products. First, plastic granules go into a heated barrel to melt and blend. Then, the molten plastic gets shot into a mold at high pressure.
The cooling starts right away, solidifying the plastic in the mold’s shape. This method allows for creating complex shapes accurately and consistently.
Key Components of Injection Molding Machinery
Connaître les machinery’s parts is crucial for good industrial output. Each piece is vital for top-notch products.
| Composant | Fonction |
|---|---|
| Hopper | Feeds plastic granules into the system |
| Screw | Moves and melts the plastic material |
| Unité de serrage | Holds the mold halves together during injection |
| Mold | Shapes the injected plastic into the desired form |
Smooth running of these parts is key for successful plastic making. Knowing and caring for these components helps make efficient, quality products.
Matériaux utilisés dans le moulage par injection
Injection molding is a key process in manufacturing. It requires careful selection of materials. Knowing the propriétés des matériaux is essential for creating the best products. We will explore two main types: thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics.
Thermoplastiques
Thermoplastics are often chosen for their ability to melt and reshape many times. This makes them perfect for designs that need change and flexibility. Companies like BASF and DuPont offer detailed guides on selecting these materials. Some well-known thermoplastics are:
- Polyéthylène (PE)
- Polypropylène (PP)
- Polystyrène (PS)
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Thermosetting Plastics
Unlike thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics harden forever when heated. Because they don’t melt again, they’re great for products needing durability and heat resistance. Here are some examples of thermosetting plastics:
- Résines époxy
- Résines phénoliques
- Mélamine Formaldéhyde
MDDI has showcased case studies of these materials in top-performing products. They are particularly used in the automotive and medical fields.
Material Selection Criteria
Comprendre propriétés des matériaux is critical for product design. You must consider strength, flexibility, thermal stability, and how it looks. ASTM provides detailed guidelines that are very useful.

Choisir le bon injection moldable plastics boosts product performance. It also increases reliability and efficiency.
| Type de matériau | Avantages | Applications courantes |
|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastiques | Flexible, Re-moldable, Wide Range | Consumer Goods, Packaging, Construction |
| Thermosetting Plastics | High Thermal Stability, Strong | Automotive Parts, Electronics, Medical Devices |
Benefits and Limitations of Injection Molding
Injection molding is a rentable way to produce large quantities. It’s perfect for making lots of parts cheaply. The accuracy and consistency of this method are unmatched.
However, it’s not without drawbacks. The initial cost for creating molds is high. This is a significant upfront expense. Also, certain design restrictions like draft angles add complexity. These might force changes that aren’t always ideal.

Choosing the right materials is another hurdle. It’s especially hard when you think about the planet. Some plastics are tough to recycle. This adds to production challenges and makes disposing of waste harder.
En regardant la rentabilité and ability to scale up production paints a mixed picture. We must balance these benefits with the production challenges et design restrictions. This gives us a full understanding of its pros and cons.
| Avantages | Limites |
|---|---|
| Production de masse Capacités | High Initial Tooling Costs |
| Haute précision et répétabilité | Design Restrictions |
| Géométries complexes | Recycling Challenges for Some Plastics |
Advanced Injection Molding Technologies
In the world of plastic making, advanced injection molding technologies have made big changes. They bring new ways to mold with great detail, make tiny products, and design with more freedom. These new methods are changing how things are made. They allow for crafting detailed and high-quality items more efficiently.
Scientific Molding
Scientific molding uses data to improve the injection molding process. It carefully controls things like temperature, pressure, and how materials flow. Doing this, we get better quality and products that are always the same. This is very important for areas that need things to be just right, like cars and planes. ICOMold is at the forefront, boosting material quality with these methods.
Micro Injection Molding
Micro injection molding is a breakthrough for making very small and detailed parts. These tiny parts are key in medicine and electronics. This method allows for creating tiny products with amazing detail. With our skills, we ensure these tiny parts are made perfectly and work well.

Gas-Assisted Injection Molding
Gas-assisted injection molding uses gases to make hollow areas and use less material. This smart process saves money and makes items stronger and easier to design. It lets makers create light but strong parts for many uses.
These new ways of making things show how plastic manufacturing is always changing. By using scientific molding, micro molding, and gas-assisted molding, we lead innovation and quality in making things. Discover the latest in efficiency and product quality with these technologies. For more info and technical details, visit ICOMold’s resources.
Conclusion
Injection molding is key in making things we use every day. It has grown and changed to meet industry needs over time. Innovations and a move towards sustainability make its future look bright.
Newer molding technologies, like scientific and micro injection molding, are changing the game. These methods improve how things are made. They allow for more detailed and precise products. Industry 4.0 technologies are also making molding more efficient and flexible to demands.
Being green is important in molding’s future too. Companies are working to make less impact on the environment. They aim to keep making high-quality products but in eco-friendlier ways. As needs change, injection molding will keep evolving. It will remain vital in making products for many years.
FAQ
What are the basic principles of injection molding?
Injection molding creates parts by injecting molten material into a mold. It consists of clamping, injection, cooling, and ejection steps. Resources from the Society of Manufacturing Engineers provide in-depth knowledge.
How did injection molding originate and develop over time?
Invented in the late 1800s, injection molding has evolved majorly. From simple items to complex parts for cars, aerospace, and electronics. The Plastics Industry Association has documented its history.
What industries commonly use injection molding?
Many industries, like automotive, aerospace, and healthcare, rely on injection molding. It’s key for producing precise, repeatable parts efficiently. Publications from the Consumer Technology Association discuss its uses.
Can you explain the injection molding process step-by-step?
Injection molding involves clamping, injecting, cooling, and ejecting. There are special methods like overmolding for added functionality. Detailed explanations are found in the Society of Plastics Engineers’ articles.
What are the key components of injection molding machinery?
Essential parts of injection molding machines include hopper, screw, clamping unit, and mold. They ensure the production of quality parts. “Principles of Polymer Engineering” covers these components well.
Quels sont les types de matériaux utilisés dans le moulage par injection ?
Thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics are commonly used materials. They’re chosen based on strength, flexibility, and other properties. Information on materials is available in BASF and DuPont datasheets.
What are the benefits and limitations of injection molding?
Injection molding is cost-effective and precise, ideal for making complex shapes. But, it has drawbacks like high tooling costs and design constraints. Analysis by the National Association of Manufacturers highlights these points.
What advanced technologies are used in injection molding?
New techniques include scientific molding, micro molding, and gas-assisted molding. They improve precision and reduce material use. The American Institute of Chemical Engineers explains these technologies in detail.