If you want to learn about what does cnc lathe stand for, you have arrived at the right place. The answer from the beginning is that CNC Lathe stands for Computer Numerical Control Lathe.
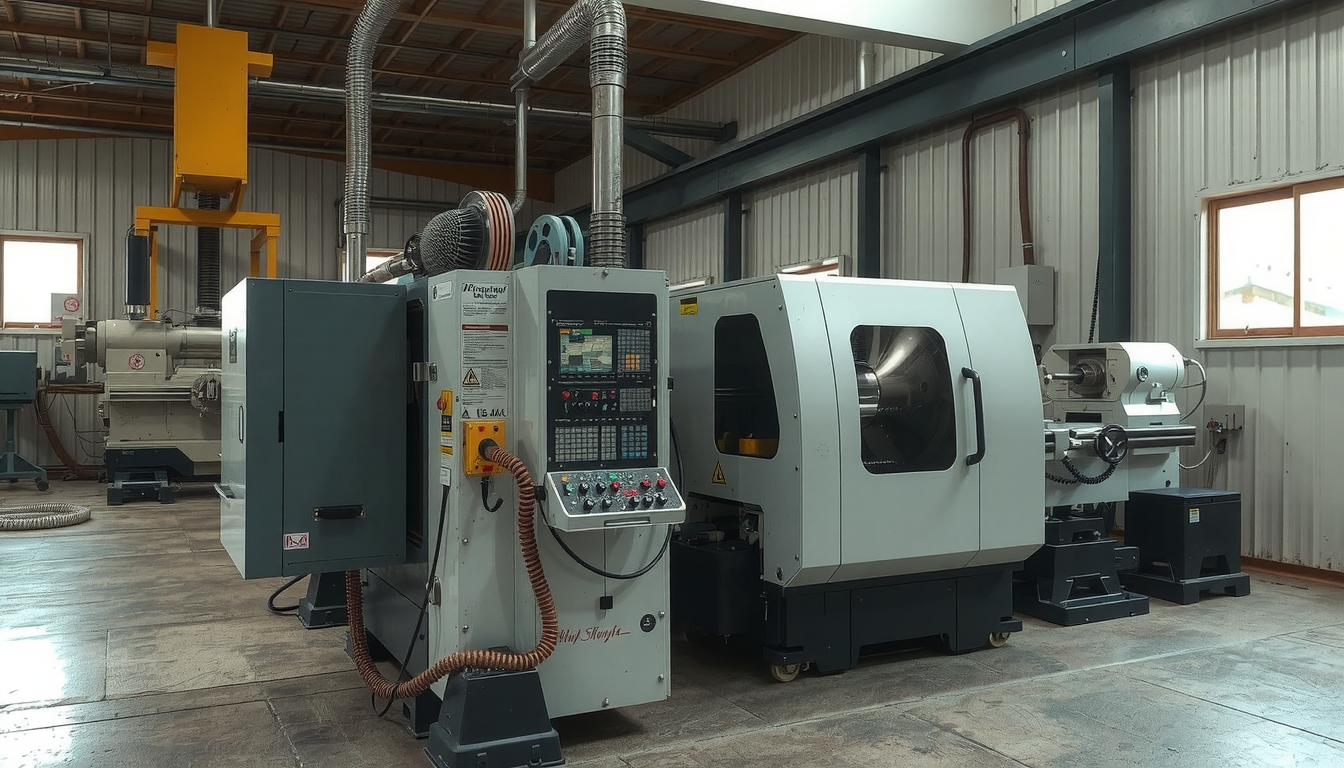

Despite the fancy term, it is easy to grasp the concept. It is similar to a traditional lathe machine but the computer control it instead. The part is made with the help of a machine that uses a program instead of a person turning wheels and pulling levers.
In this guide, we will break down the name into two parts: “CNC” and “Lathe.” We will see how they work together in one whole system. We will trace the steps from a computer file to a finished part. We will also discuss the role played by these machines in our lives.
Breaking Down the Name: What Does “CNC” Mean?
Before we can start working with the complete term, it is important to know what “CNC” actually is. This is the technology that allows the machine to run without any human intervention. It uses a process called Computer Numerical Control.
Computer Numerical Control Explained
Let’s deconstruct the name step by step.
- Computer: The core of the system is a computer. It’s the one that receives the instructions saved in the computer file.
- Numerical: Numbers and coordinates are the components of the messages sent by the computer. They define the exact commands for the machine including the speed of the motor, the tool, and the movement.
- Control: The computer is in charge of the precise functions like opening the motors and setting variables. It executes the program perfectly every time.
This technology evolved from an older system known as “NC,” or Numerical Control. This system was different as it read punched tape instead of computer files.
For example, you can think of it as a modern player piano. A classic player piano was a paper roll with holes to play notes. A CNC machine does the same but instead of just a music sheet it uses a computer program that tells it exactly where to cut metal or plastic. This is the meaning of CNC in any context.
The “Lathe” Part: A Key Tool in Making Things
Let us then move to the next half of the name, which is “Lathe.” A lathe is one of the oldest and most important machine tools.
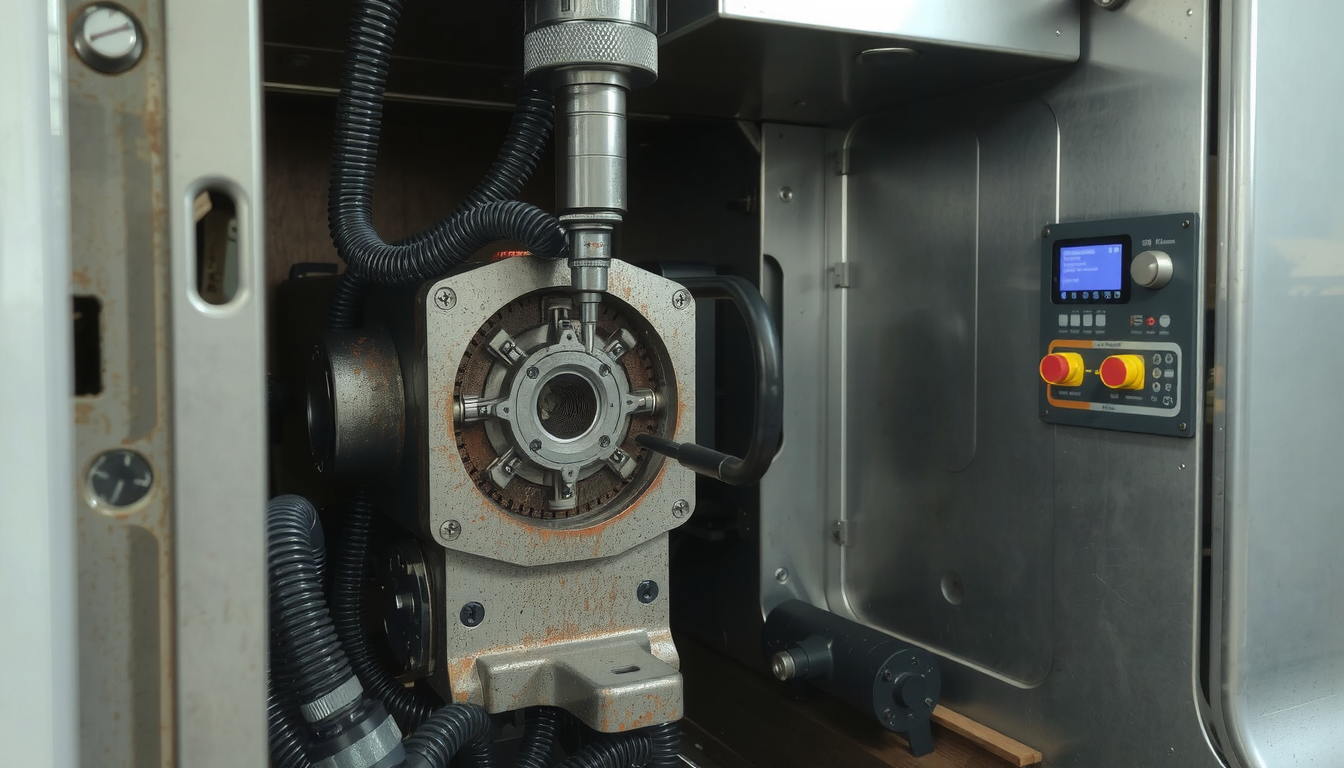
The principle behind a lathe is that it can shape a material using fast rotation. A cutting tool that does not move is pressed against the spinning material to sculpt away material creating the desired shape.
You can easily visualize it as a potter’s wheel—wherein, a potter turns a lump of clay and manipulates it by hand into a bowl shape. Likewise, a lathe turns a potter. In this case, it spins a piece of metal, plastic, or wood while using a sharp tool instead of hands. This method is efficient for making rotational or tubular shapes.
Putting It All Together: So, What Is a CNC Lathe?
Having discussed both parts, we can now build our understanding around the two concepts. A CNC lathe is a machine that uses the computer to perform operations like turning, facing, drilling, and cutting automatically. It adds the automation of the digital technology to the traditional lathe’s functionalities.
With a CNC lathe, an operator usually flips the script on the traditional job. No more cranking levers to produce cuts by hand. The operator instead works as a programmer and a supervisor. They load the program, configure the machine, and monitor the whole operation.
The exquisite precision and fast performance of the production processes are attributed to this technology. The standard industrial practice for large scale identical components or intricate forms to be created is by Services de tournage CNC. Thus, a CNC lathe is the gateway to modern production.
| Fonctionnalité | Manual Lathe | Tour CNC |
|---|---|---|
| Contrôle | Manual handwheels and levers | Computer program (G-code) |
| Précision | Dépend de la compétence de l'opérateur | Extremely high and consistent |
| Répétabilité | Low; each part is unique | Very high; identical parts |
| Complexité | Limited to what an operator can do | Can produce highly complex geometries |
| Vitesse | Slower, one part at a time | Much faster, ideal for production runs |
| Operator Skill | Requires a highly skilled machinist | Requires programming & setup skills |
From Computer File to Real Part: The CNC Lathe Process
One effective way to understand how the CNC lathe works is to run through an example process. For example, what are the stages for a simple idea to become a finished metal part? The process can be broken down into five main steps. This is a practical demonstration of this synergy of technology from design to manufacturing.
Step 1: The Blueprint (CAD Design)
Everything starts with a blueprint in the computer. An engineer or designer creates a 2D drawing or a 3D model of the part using CAD software. CAD stands for Computer-Aided Design. This is the virtual blueprint for the final product.
Step 2: The Instructions (CAM & G-Code)
Next, the CAD model is loaded into CAM software. CAM stands for Computer-Aided Manufacturing. The CAM software is very smart. It plans the best way to cut the part. This includes which tools to use and the path they should take.
It then changes these plans into a language the CNC lathe can understand. This language is called G-code. G-code is a list of commands that tell the machine every single move to make.
Step 3: The Setup
The G-code program is uploaded to the controller of the CNC lathe. Then the operator takes a raw type of material block, typically a metal rod. They secure it with a clamp in the lathe’s chuck tightly. They also install all the necessary cutting tools to the turret of the machine.
Step 4: The Automation
At the press of a button, the operation starts. The CNC lathe performs as instructed by the G-code without errors. The material begins to rotate. The tools engage to face, turn, drill, and shape the workpiece. This is all done automatically with no further assistance from the operator.
Step 5: The Final Product
As soon as the program is done, the machine comes to a halt. The operator can now remove the finished part. The part will go through an inspection to verify that it is of the exact dimensions as per the original design. The part is now a complete, accurate piece and is available for use.
Parts of a Modern CNC Lathe: Key Components
To have a clear picture of what a CNC lathe is, it will help you to know the differences of its main parts. These parts consist of a system of automated specialized machines.
- Contrôleur : The controller is the “brain” behind the machine. It is a computer that interprets the G-code, sends electrical signals to the motor and other parts of the machine.
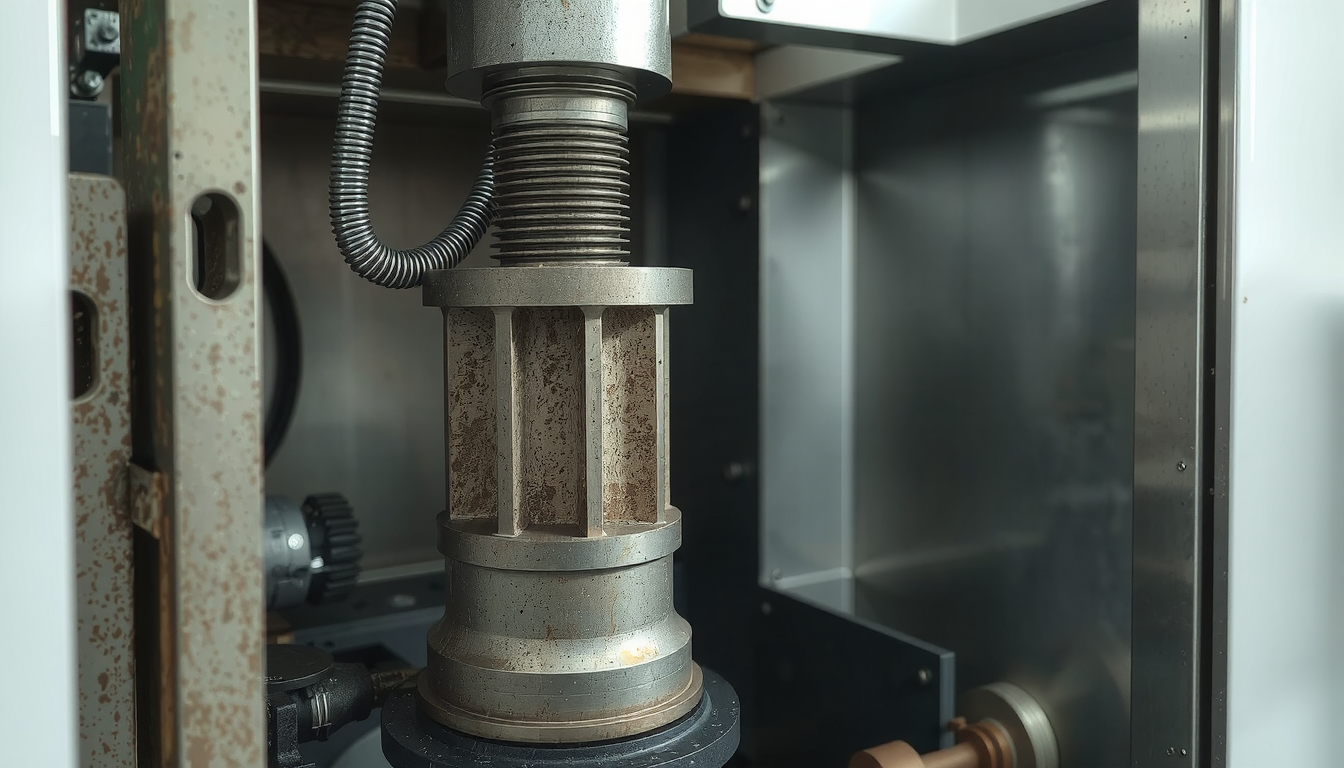

- Spindle & Chuck: The spindle is the rotating part of the lathe. The chuck is mounted on the spindle acting like the hand of the lathe. It clamps the workpiece and keeps it rigid while it rotates.
- Turret & Tooling: This is like the machine’s set of “hands.” The turret is a disc that spins and has places for different tools. In case it is time to use a new tool, the turret quickly rotates until the right one is positioned. A tool that is tangibly secure has a distinct ‘click’ sound that one can hear while seating it into the turret during tool changes.
- Bed & Ways: The bed is the heavy, rigid “skeleton” of the machine. It is the basis of the machine That weight creates a stable platform for the bed and helps to dampen the vibration. The ways are the smooth, precise rails that the moving parts slide on.
- Drive Motors & Ball Screws: These are the “muscles.” Powerful motors turn in response to the controller’s signals. They are connected to ball screws, which are special threaded rods. These convert the motor’s rotation into very precise straight-line motion for the tools.
Real-World Impact: Where Are CNC Lathes Used?
After you learn the meaning of CNC lathe, you will feel like it’s time to track its applications. They are present almost everywhere.
Modern manufacturing largely depends on CNC lathes. They are the builders of the highly precise, durable parts we all need. Many companies both big and small depend on professionals, like Mékalite to produce significant components with the help of this technology. The global market for CNC lathes was over $15 billion in 2023. That figure indicates the importance of CNC lathes in the production sector.
Here are just a few industries that depend on CNC lathes:
- Aérospatiale : For its engine shafts, landing gear components, and special fasteners that can only be made with incredible strength and precision.
- Automobile : For the making of engine pistons, driveshafts, brake components, and suspension parts.
- Médical : For the production of surgical implants like total hip joints, and precise tools for surgeons.
- Électronique : For tiny, complex connectors, sockets, and housing through devices.
Conclusion: More Than Just An Acronym
So, what does cnc lathe stand for? To put it succinctly, it is an acronym for Computer Numerical Control Lathe. However, it is more than just that.
The productive combination of a classical machine tool and modern computer automation is represented by this acronym. This combination guarantees the production of a level of quality, speed, and complexity that was previously unattainable. The comprehending of the CNC lathe brings out knowledge of the whole production processes that is difficult to learn outside.
FAQ: Your CNC Lathe Questions Answered
What’s the main difference between a CNC lathe and a CNC mill?
The difference lies in what is the part that moves. In a CNC lathe, the work materials rotate, causing a fixed tool to cut the part. This makes it most suitable for cylindrical or round shapes. On the contrary, a CNC mill is one where the tool is the rotating part and the material piece is fixed. This is better for making flats, pockets, and more complex shapes.
Is it possible for a beginner to run a CNC lathe?
Certainly, however it demands a great deal of commitment to study and practice. With the advent of modern software, things have become a bit easier now. But you will obviously need to acquire the necessary knowledge such as the safety rules, the basics of machining, and G-code programming which are crucial. Additionally, a number of community colleges and online resources are offering beginner courses.
What materials can a CNC lathe work with?
CNC lathes are known for their great flexibility. They are also able to process many different materials. This list includes metals like aluminum, steel, brass, and titanium. Moreover, some grades of plastics like ABS, nylon, and polycarbonate are also suitable. Some of them can even cut wood.
What is G-Code?
G-code is a programming language that controls how a CNC machine operates. It is a series of text commands. Each command line instructs the operations. For instance, one of the lines would say that the tool has to move to an X/Z coordinate. The spindle might be the next line setting the turning on with the speed given.
Why would a company use CNC lathe services instead of buying a machine?
Because CNC lathes are not only expensive but also demanding in terms of workspace, maintenance, and operator skills; it is often a better idea for a lot of companies to use CNC lathe service. Making it possible for them to access, top machinery, and skilled machinists, without a huge capital gain, this model is particularly appropriate for prototypes or small production runs.

