CNC Swiss turning is a way to make specialized and very tiny, complex, and lengthy parts with precision. It got its name from the machines which were initially used in Switzerland to create tiny, precise watch components. The most important part is a sliding headstock that brings the material through a guide bushing. It provides significant support directly where the cutting occurs.
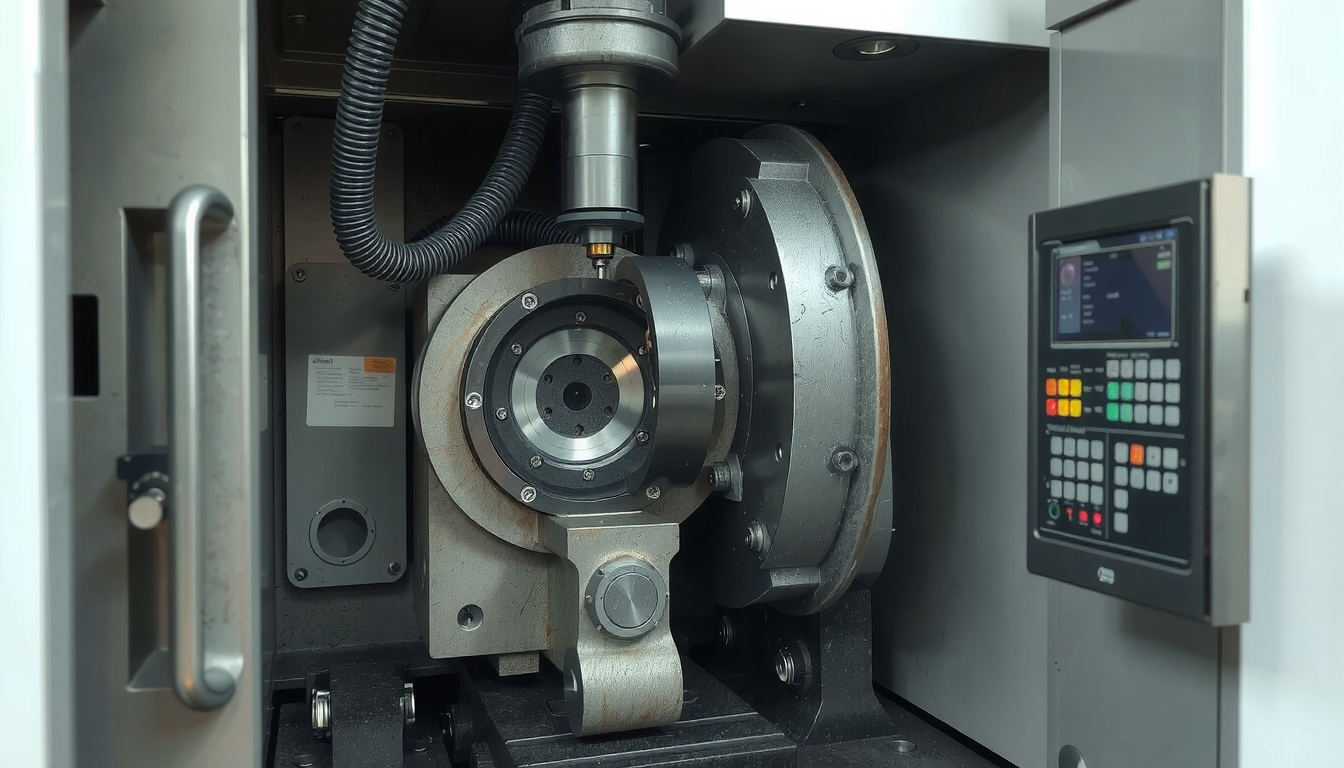

This special method allows for high precision and complexity of design. In this guide, we will discuss the CNC Swiss turning process and highlight its benefits. We will also cover its best applications and guide you on how to find the right partner for your project.
H2: What is CNC Swiss Turning and How Does It Work?
Learning about CNC Swiss turning involves knowing how it differs from a standard lathe. The primary difference is the mobility of the material and the tools. This unusual movement results in the process’s main advantages for certain parts.
H3: The Core Principle: A Sliding Headstock
In a typical lathe, a part is held in a chuck and spins while tools move along it to cut away material. This is satisfactory for shorter, thicker components, but not for long and slim parts, as they may bend or vibrate from the force of the cutting tool.
CNC Swiss turning was an ingenious solution for this problem. The machine feeds a spinning bar of raw material through a guide bushing. The cutting tools are mounted strikingly close to this guide bushing. The material shifts; the tools do not. The part is thus supported precisely at the cutting point. This mechanism retards bending and vibration, which is the secret to its high accuracy.
H3: A Step-by-Step Look at the Process
The production is highly automated and efficient, making it the best-case scenario for making large quantities of parts. While details can vary, Swiss machining is a high-precision CNC process that generally follows these steps:
- Bar Feeding: A long bar of raw material, called bar stock, is loaded into a bar feeder. The feeder automatically pushes the stock into the Swiss machine as needed.
- Guide Bushing Support: The bar stock moves through the guide bushing. This bushing holds the material firmly. It provides rigid support at the point of the cut.
- Main Spindle Machining: The headstock holds and spins the bar. It slides along the Z-axis. This pushes the material past the stationary tools. This can perform turning, drilling, and milling operations on the front of the part.
- Sub-Spindle Operations: After the front side is done, the part is often handed off to a second spindle. This is called a sub-spindle. This spindle grabs the part and allows for work on the back side. Operations on the main and sub-spindle can happen at the same time. This saves a lot of time.
- Part Ejection: Once all operations are complete, the finished part is cut from the bar stock. It falls into a parts catcher. The machine immediately starts the process over for the next part.
H2: Swiss Turning vs. Conventional CNC Turning: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Choosing between CNC Swiss turning and conventional turning depends entirely on your part’s design. Every process has its own precise advantages. Knowing what distinguishes them will empower you to pick the most effective and affordable method for your project.
H3: Choosing the Right Process for Your Part
The most crucial factor is usually the part’s shape, including its length compared to its diameter. The table below breaks down the key differences to help you decide.

| Fonctionnalité | CNC Swiss Turning | Conventional Service de tournage CNC |
|---|---|---|
| Workpiece Support | Guide bushing supports stock next to the tool. | Workpiece held at one or both ends (chuck/tailstock). |
| Ideal Part Profile | Long, thin parts (high length-to-diameter ratio, >4:1). | Shorter, larger-diameter parts (low length-to-diameter ratio). |
| Precision & Rigidity | Extremely high; very little deflection. | High, but can deflect on long, thin parts. |
| Complexité | Great for complex parts with milled features in one setup. | Good, but may need extra steps for complex features. |
| Durée du cycle | Often faster for complex parts due to simultaneous operations. | Can be faster for simple, large parts. |
| Temps de préparation | Generally longer and more complex. | Usually faster and simpler. |
| Rapport coût-efficacité | Best for high-volume production of complex small parts. | Good for prototypes, low-to-mid volumes, and larger parts. |
H2: Key Advantages of the CNC Swiss Turning Process
The unique mode of operation of a Swiss machine yields several key benefits. These advantages make it the preferred method for demanding applications where precision and complexity are of utmost importance.
H3: Unmatched Precision and Tight Tolerances
The guide bushing’s support is the key. By cutting the material right as it exits this support, any bending or vibration is practically eliminated. This stability paves the way for outstanding accuracy. It is common for CNC Swiss turning to achieve tolerances of ±0.0002 inches (±0.005 mm). This level of precision is essential for parts used in medical devices and aerospace systems.
H3: “Done-in-One” Machining for Complex Parts
Modern Swiss machines are much more than just lathes. They are multi-axis turning centers with “live tooling”—powered tools that can mill, drill, and tap. Combined with a sub-spindle for back-work, a complex part can be completely finished in a single cycle. This “done-in-one” approach often removes the need for extra setups, which lowers costs and enhances part-to-part consistency.
H3: Superior Performance on Long, Slender Parts
This is the classic application for CNC Swiss turning. For parts with a length-to-diameter ratio greater than 4:1, it is often the only viable method. On a conventional lathe, such parts would bend away from the tool, leading to poor accuracy and finish. The Swiss method is a cutting-edge precision machining process that solves this fundamental problem.
H3: Excellent Surface Finishes
Vibration is the enemy of a smooth surface finish. Because the guide bushing provides such rigid support, vibration is kept to a minimum during cutting. This results in parts with excellent, smooth surfaces right off the machine. This can often eliminate the need for secondary operations like grinding or polishing, saving both time and money.
H2: Design for Manufacturability (DFM): Tips for CNC Swiss Turning
Designing a part with the manufacturing process in mind can save you time and money. When working with CNC Swiss turning, a few key considerations can make a big difference in the final quality and cost of your components.
H3: Material Considerations
The quality of the raw material is very important in Swiss turning. We recommend using high-quality, straight bar stock. From our experience, using ground bar stock instead of standard extruded stock can dramatically improve concentricity and overall precision. Any variation in the bar’s diameter can affect how it fits in the guide bushing, which can impact accuracy.
H3: Tolerance and Feature Design
Tolerances define how much a part’s dimension can vary. While Swiss machines can hold very tight tolerances, you should only specify them where they are truly needed. Overly tight tolerances on non-critical features can increase cycle time and drive up costs. Also, try to design features that can be made at the same time. For example, a milled flat can be cut on one side while a drill works on the other. This improves efficiency.
H3: Leveraging Multi-Axis Capabilities
Think about your part in a “done-in-one” context. Design features so they can be completed on the main and sub-spindles in one continuous process. This reduces the need to move the part to another machine, which lowers the risk of error and reduces total production time. Our engineers can help you review your design to find opportunities for optimization.
H2: Industries and Applications Fueled by CNC Swiss Turning
The precision and complexity offered by CNC Swiss turning make it essential for many of today’s most advanced industries. The ability to produce small, intricate parts reliably is critical. The types of parts are typically produced on Swiss CNC lathes span a wide range of applications.
- Medical & Dental: This is one of the largest markets for Swiss-turned parts. Examples include bone screws, surgical instruments, dental implants, and tiny components for diagnostic equipment.
- Aerospace & Defense: The need for reliability and precision is absolute. Parts include high-pressure fittings, electrical connectors, sensor housings, and components for guidance systems.
- Électronique : As electronics get smaller, so do their components. Swiss turning is used for connector pins, sockets, fiber-optic parts, and tiny shafts for micro-motors.
- Automobile : Key components in modern vehicles require high precision. These include fuel injector nozzles, parts for ABS braking systems, and small transmission shafts.
- Hydraulics & Pneumatics: The performance of hydraulic and pneumatic systems depends on tightly toleranced parts. These include valve spools, small pistons, and fittings.
H2: Choosing the Right Partner for Your Swiss CNC Turning Services
Selecting the right manufacturing partner is just as important as the process itself. A good partner brings not only the right equipment but also the experience and quality systems to ensure your project’s success.
H3: Key Evaluation Criteria
When you look for a supplier for your Swiss turning needs, consider these points:
- Technical Capabilities: Do they have machines with the right diameter capacity and axis count for your part’s complexity?
- Expérience dans le secteur : Have they made parts for your industry before? A shop with medical experience will understand the strict quality and material rules.
- Quality Systems: Are they certified to quality standards like ISO 9001 or AS9100 for aerospace? This shows a commitment to quality control.
- Soutien à l'ingénierie : Do they offer design for manufacturability (DFM) feedback? A good partner will help you optimize your design for better quality and lower cost.
H3: Why Mekalite is Your Trusted Partner
At Mekalite, we combine modern equipment with decades of hands-on expertise to deliver superior results. Our Services de tournage CNC suisse are built to meet the toughest demands of today’s leading industries. We see ourselves as your partner, not just a supplier. We work with you from design to delivery to guarantee your project is a success. Learn more about our deep commitment to quality and innovation at Mekalite.com.
H2: FAQ: Your CNC Swiss Turning Questions Answered
Here are answers to some common questions about CNC Swiss turning.
H3: What is the main difference between a Swiss lathe and a regular CNC lathe?
The biggest difference is how the material is held and moved. A Swiss lathe moves the material through a guide bushing for maximum support. This is best for long, thin parts. A regular lathe holds the part still in a chuck and moves the tools to it. This is better for shorter, larger parts.
H3: What materials can be machined with CNC Swiss turning?
A wide range of materials can be used. This includes stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, brass, copper, and plastics like PEEK and Delrin. The most important thing is that the material is available as a long, high-quality bar.
H3: Is CNC Swiss turning expensive?
The setup cost can be higher than for conventional turning. But for complex parts in medium to high volumes, it is very cost-effective. This is because it finishes the part in one setup, which reduces cycle time and eliminates the need for other operations. The machines can also run “lights-out” (unattended) for long periods, further increasing efficiency.
H3: What is the typical part size for a Swiss machine?
Swiss machines are best for small parts. They typically handle diameters from 0.5mm (0.020″) up to about 38mm (1.5″). They are a perfect fit for parts where the length is at least four times greater than the diameter.
H3: Can a CNC Swiss machine perform milling?
Yes. Modern CNC Swiss machines are multi-axis turning centers. They have “live tooling,” which are powered rotating tools. These tools can perform milling, drilling, tapping, and engraving. This allows for the creation of very complex parts in a single setup.

