A CNC lathe refers to a machine tool controlled by a computer that shapes raw materials. A workpiece rotates, and a cutting tool applies a force against it. Barcode readers are turned into precise, circular shapes with this technique.
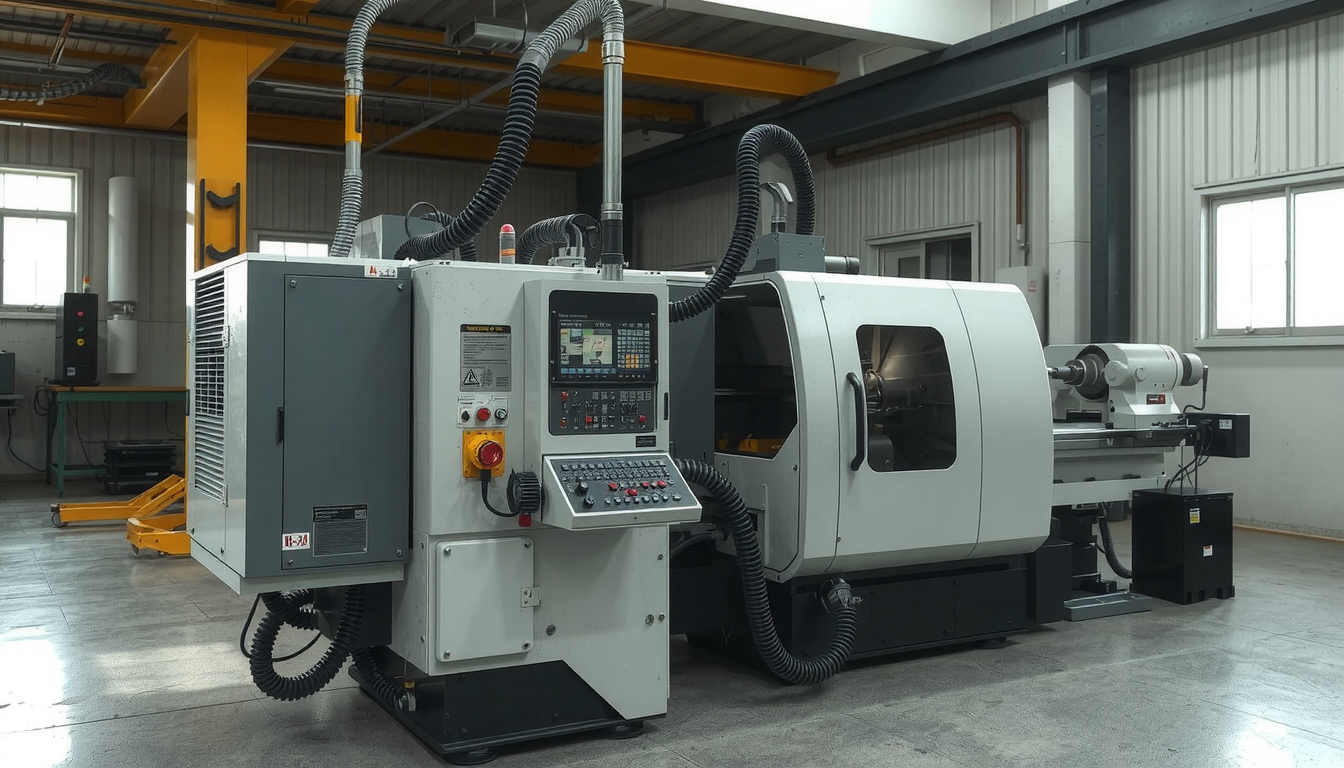

A manual lathe needs the operator’s intervention. But with a CNC lathe, there is automation instead. It emphasizes the industrial process, accuracy, and repeatability. A CNC lathe can flawlessly make the same component over and over again, even thousands of times. This is possible by combining the principles of an old-style lathe with the latest computer programming.
In this guide, we will cover everything regarding a CNC lathe. You will find out its main parts. You will also view how it operates. You will see what it is capable of manufacturing. Also, at the end, you will learn how to select the one that suits your needs the best.
CNC Lathe Operating Principle
You can imagine a CNC lathe as a potter’s wheel for cutting hard materials. Instead of molding clay with your hands, the machine gets a sharp tool. This tool cuts out a part of the material of a workpiece that is spinning.
This primary operation has two essential motions. The first thing is that the workpiece spins at high speed. The second thing that happens is that the cutting tool moves along two lines or axes.
- X-axis: The tool goes in and out. This is what is controlling the part’s thickness.
- Z-axis: The tool shifts left and right. This will affect the length of the part.
This specific process is also called “turning.” Thus, controlling the motions of only two axes of movement, a CNC lathe can achieve forming various shapes. It can produce parts that are cylindrical, frustum, or spherical. The combination of turning and accurate tool movement allows the machine to work with metals and other materials.
KEY COMPONENTS OF A CNC LATHE
In order to go deeper into the principles of a CNC lathe function, we should first introduce its components. Each part has a specific duty. Working together, they form a powerful and locked system. Familiarizing yourself with these items is key to being aware of the machine’s capabilities.
You can find a breakdown of the primary CNC lathe components along with their respective functions if you want. The most significant components are the following:
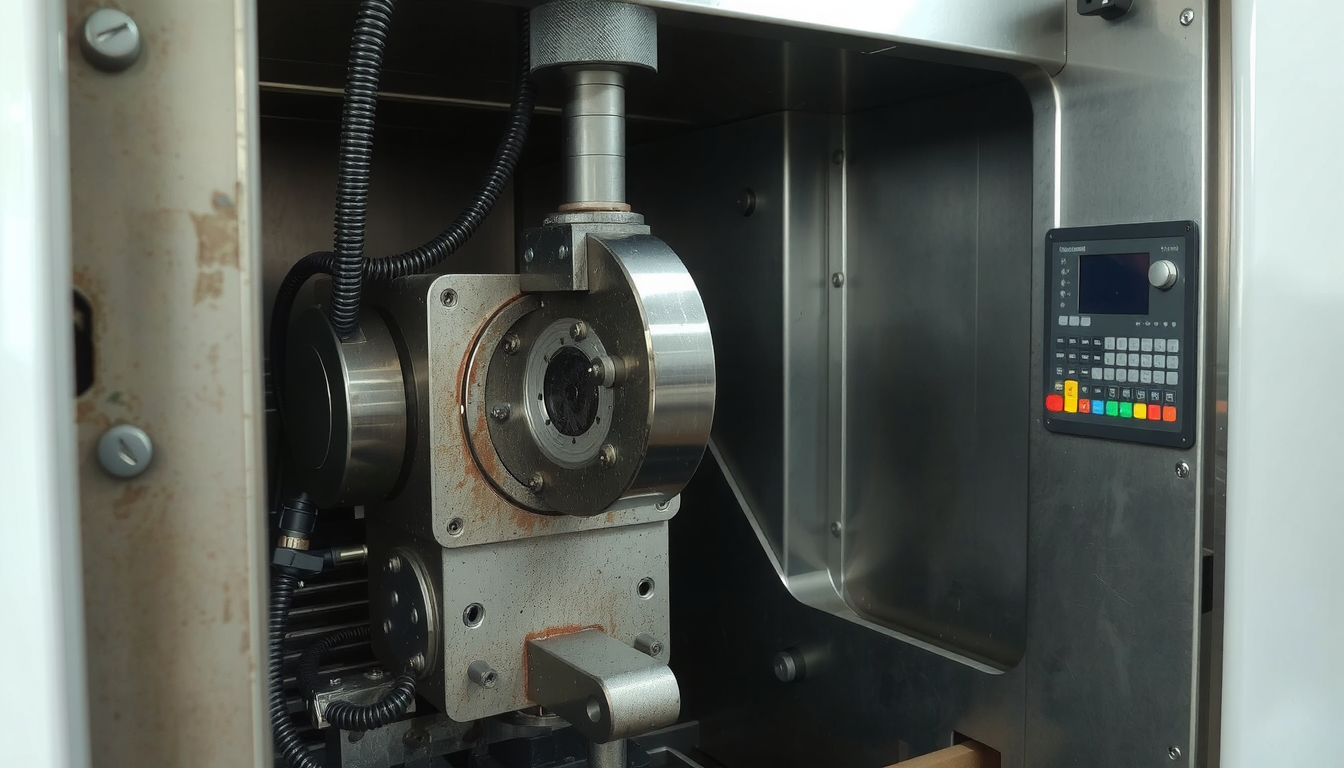
- Headstock
The headstock is the powerhouse of the lathe. It comprises the main motor, gears, and the spindle. Consequently, it gives the workpiece the power to turn. - Spindle & Chuck
The spindle is the rotating shaft. It is conjoined to the spindle, which gives it the ability to clamp the material on the chuck. The chuck is responsible for securely holding the workpiece while it spins. - Tailstock
The tailstock is found at the opposite side of the headstock. This end supports the component. It is necessary for the stability of long or slender workpieces during turning by holding them straight and thus preventing them from warping. - Bed
The bed is the robust and stable part of the machine’s structure. It aligns the other components as well, such as the headstock and the tailstock. The right alignment is the key to the production of good workpieces. - Carriage & Tool Turret
The carriage is the assembly that shifts the cutting tool across the X and Z axes. The tool turret is the one that sits on the carriage. This turret comprises numerous cutting tools. The tool turret’s capability of rotation adds automation to the machining process, thus it can shift between the tools for different jobs, like cutting, finishing, or drilling. - CNC Control Panel
The CNC control panel is the brain of a CNC lathe. It is a computer interface that the operator uses to load the program, make adjustments, and supervise the entire machining process.
From Digital Design to Physical Part: A CNC Lathe Workflow
CNC lathe parts are manufactured using a method that is digital design-driven and mechanical work-centered. The process is a sequence of steps from making the design to the final product. Designers see these stages as a seamless flow from an idea to the real, physical product.
- The CAD Model
Everything begins with a digital design. The designer creates a 3D model of the part using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This digital representation includes all the features and sizes that the final part will need. - CAM Programming
In this next step, the 3D model is then transferred to a CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) program. This application enables the programmer to set blade paths. The programmer chooses the tools for usage, determines how fast the material will spin, and how fast the tool will cut. The CAM software then provides the G-code instructions which correspond to these parameters. This is the programming language that the CNC lathe is programmed in and the only one that it understands.
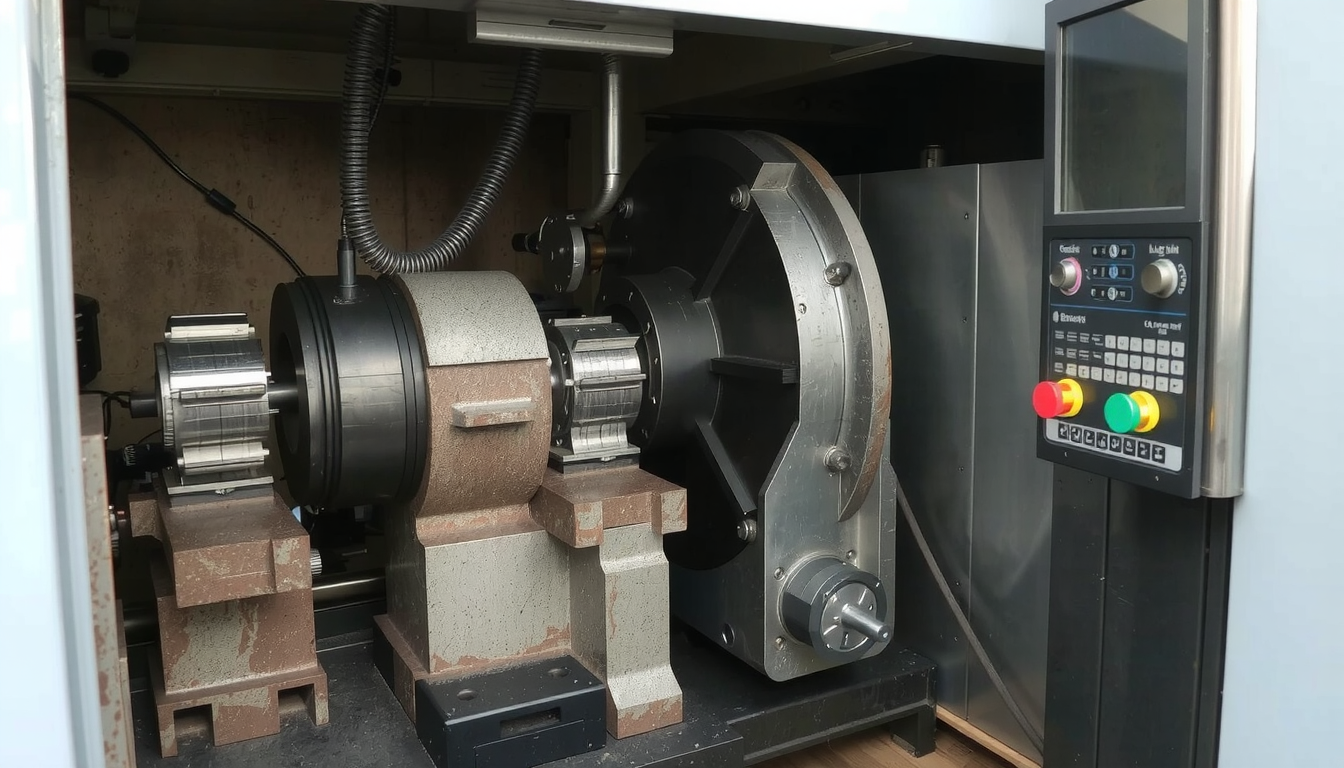
- Configuración de la máquina
The digital model comes to life here in a physical machine. An experienced technician prepares the CNC lathe. After putting a piece of raw material inside the chuck, they proceed to load the correct cutting tool into the tool turret. Here, a critical step is setting the “offsets.” This is where the machine is told the exact position of the workpiece and the tips of every single tool. By doing this, absolute accuracy is confirmed. - Running the Program
After the machine is in position, the technician proceeds to upload the G-code program to the CNC controller. Prior to starting, a simulation or “dry run” is always done. This moves the tools without making any cuts in the air checking for potential crashes or errors in the program. After confirming that everything is okay, the operator shuts the safety doors and runs the program. The machine, therefore, initiates the automatic process of cutting the part. - Quality Control & Finishing
After the CNC lathe has accomplished its task, and the part is taken out to be inspected thoroughly. The operator uses precision tools such as calipers or micrometers to take measurements and confirm that the part meets the specifications mentioned in the CAD model. Some parts may be left with a few finishing operations, like the removal of sharp edges.
The whole procedure for intricate components is handled by expert professionals who are offering cnc lathe services.
What Can You Make with a CNC Lathe? Industries and Applications
A CNC lathe is a basic tool in many industries due to its flexibility. It can make a very large quantity of round parts with high precision. The ability to keep tight tolerances, which are often within ±0.005 mm (or 0.0002 inches), is vital for high-performing uses.
Here are some good examples that show you the production capabilities:
- Aeroespacial: Shafts for engines, fittings for high pressure, and landing gear parts. They all need to be strong and without defects.
- Automóvil: Engine parts are pistons and valves, driveshafts, and suspension parts. Making these numbers with a CNC lathe is an excellent choice.
- Médico: Custom surgical instruments, bone screws, and implants made of titanium. Precision cutting via the CNC machine is crucial for patient safety.
- Electrónica: Small connectors, audio equipment’s custom knobs, and sensor’s protective housing that prevents damage from the ambient.
- Oil & Gas: Stress-resistant valves, flanges, and parts which are used in drilling tools exposed to judicious conditions.
The Right CNC Lathe Selection: A Personal Guide
Choosing the right CNC lathe is strictly based on the requirements of your project. There can’t be a universally accepted “best” machine. Rather, you need to align the machine’s potential with your specific objectives. This guide is a valuable tool for you that will help you in making the correct decision, whether you are buying a machine or selecting a manufacturing service.
Axis Configuration
The CNC lathe’s number of axes denominator the complexity and capability to produce a product.
- 2-Axis: A 2-Axis CNC Lathe is the most basic that has X and Z axes for basic turning and facing operations. It is best for simple round parts such as shafts and pins.
- 3-Axis (with Live Tooling): It adds a C-axis (rotation of the workpiece) and “live tools” (tools that are rotating, such as drills or end mills). This allows for off-center drilling, milling, and tapping, all in one setup. This is ideal for more complex parts with features like slots or flat faces.
- Multi-Axis: These machines, also termed turning centers, can be as much as 4, 5, or even more axes. They may include a second spindle (sub-spindle) to work on the rear side of a part. The machines are for the most complex parts. This helps reduce set-up time and raises productivity.
Key Considerations for Your Project
Use this table to weigh your options:
| Consideración | 2-Axis Lathe | 3-Axis Lathe (Live Tooling) | Multi-Axis Turning Center |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complejidad de las piezas | Simple, round shapes. | Round parts with off-center features. | Highly complex parts, all-in-one machining. |
| Volumen de producción | Good for prototypes and high-volume simple parts. | Good for medium-volume complex parts. | Best for high-volume, complex production. |
| Tipo de material | Handles most materials well. | Handles most materials well. | Best for hard-to-machine, exotic materials. |
| Budget | Lowest cost. | Moderate cost. | Highest cost. |
Take a moment to reflect on the shape of your part. Count how many you would like to make. Look at the material and budget. This will help you select a type of CNC lathe for your particular job.
Conclusion: The Precision and Automation Power
A CNC lathe has become one of the landmarks of modern manufacturing. The strength and reliability arise from milling, speed, and automation. Therefore, they can produce intricate components that are, in reality, out of this world.
We have observed how CNC lathes change files that were created digitally into high-precision mechanical parts. Even if you are a startup or a huge corporation, knowing about this technology will help you to develop ideas into reality. Every day at Mekalite we are making magic with this power, providing high-quality results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about a CNC Lathe
What is the main difference between a CNC lathe and a CNC mill?
The big difference between these two machines is what spins. On a CNC lathe, the workpiece spins while a mostly stationary tool cuts it. This is suitable for round or cylindrical parts. On a CNC mill, the cutting tool rotates and moves across a stationary workpiece. This is helpful in creating flat surfaces, pockets, and more complex shapes.
Can a CNC lathe work with materials other than metal?
Yes, absolutely. While a CNC lathe is famous for machining metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium, it also works very well with other materials. It can cut plastics like Delrin and PEEK, wood, and even some composites. The key is using the right cutting tools and setting the correct speeds for each material.
What is G-code?
G-code is the basic programming language for all CNC machines, including a CNC lathe. It is a series of commands that tell the machine exactly what to do. These commands control where the tool moves, how fast it moves, and what path it should follow to cut the part correctly.
How accurate is a CNC lathe?
Modern CNC lathes are extremely accurate. A standard machine can easily hold tolerances of ±0.0005 inches (about ±0.013 mm). High-end, precision models can do even better. This remarkable accuracy is one of the reasons that these devices are used for some critical parts in the aerospace and medical fields.
Do you need to be a programmer to operate a CNC lathe?
Not necessarily. While knowing G-code is beneficial, modern CAM software largely takes care of the programming. A proficient operator’s primary concerns are setting the machine, uploading the program, and observing the cutting procedure. Therefore, operator skills are at least as important as programming skills.

