Welcome to this easy-to-follow guide on injection molding. It’s a method that changes the way we make lots of products. Things like toys and medical devices are made with it. In this guide, we’ll cover the basic ideas, history, and parts of injection molding. This will give newcomers a good start in understanding this field.
Key Takeaways
- Injection molding is a crucial manufacturing process utilized in various industries.
- This guide offers a concise overview for beginners looking to understand injection molding techniques.
- We will delve into the history, key components, and phases of the injection molding process.
- Understanding injection molding enhances knowledge of plastic fabrication and industrial production.
- The guide also discusses the importance, applications, challenges, and future trends of injection molding.
What is Injection Molding? Understanding the Basics
Injection molding is a key process used to make parts by injecting material into a mold. It’s great for making many identical items quickly. This method uses thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics. These are heated until liquid and then shot into a mold system.
Definition and Overview
This process heats up thermoplastics or thermosetting plastics until they’re soft. Then, the soft material is pushed into a mold cavity by an injection unit. Inside the mold, it cools and hardens, taking the shape of the mold. This lets us make complex and detailed parts.
History of Injection Molding
Injection molding started in the late 1800s. John Wesley Hyatt made the first machine in 1872. It was originally for molding celluloid, an early plastic. Since then, technology has made it much better. Today, we have advanced machines for creating detailed parts for many fields. These machines use updated plastic mold design and material science.
Key Components of the Injection Molding Process
An injection molding machine has key parts critical to its operation. These include the clamping unit, injection unit, and mold system.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Clamping Unit | Holds and stabilizes the mold during the injection and cooling phases. |
| Injection Unit | Heats and injects the molten material into the mold cavity. |
| Mold System | Shapes the molten material into the desired form and facilitates cooling and solidification. |
Understanding the main parts and what they do helps us see how injection molding works. This insight shows the detailed work needed to make various precise parts consistently.
The Importance of Injection Molding in Manufacturing
Injection molding has totally changed how we make things in big numbers. It lets makers create lots of products quickly and exactly. This is key for making sure each product is the same high quality and costs less to make. Using precise methods means every part is just right, very important for industries that need the best.
Injection molding can make parts with complicated shapes easily. Other ways of making things can’t always do this well. It means companies can come up with new, custom products.
It’s also a great way to save money. It uses materials wisely and makes things more cheaply, which is better for budgets. Plus, there are many materials to choose from, making parts that last a long time for different uses.
Another plus is not needing much finishing work. Parts are almost ready to go right when they come out. This makes making things faster and adds to being able to make a lot at once.
So, injection molding is essential for making lots of things well and efficiently. It’s great for making complex parts cheaply and keeping quality consistent. It plays a big role in today’s manufacturing.
How Injection Molding Machines Work
Injection molding machines are modern marvels, built to create high-quality plastic parts. These machines are essential in manufacturing. They have an intricate design that makes production efficient.
The Parts of an Injection Molding Machine
These machines have key parts like the plasticizing unit, mold clamping systems, and the ejection mechanism. Each has a critical role in shaping products.
- Plasticizing Unit: It melts and mixes the plastic to get it ready for molding.
- Mold Clamping: The clamping unit uses hydraulic power to hold the mold tightly. This ensures accuracy during injection.
- Ejection Mechanism: Once cooled, this part pushes the finished product out. It makes the mold ready for more production.
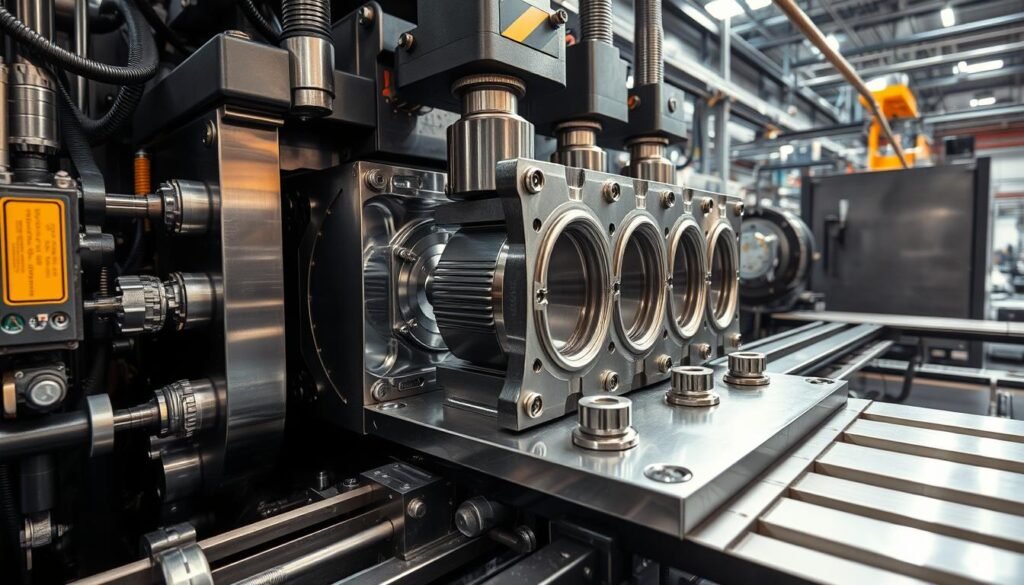
The Injection Phase
The hydraulic power behind the plasticizing unit drives molten plastic into the mold. This process needs to be fast and precise. The goal is to fill the mold quickly without losing part quality.
The Cooling and Ejection Phases
After filling, the plastic cools and hardens. Fast cooling is important to keep cycle times short. This boosts productivity without compromising the product’s quality.
Strong mold clamping prevents flaws by keeping the mold closed during cooling. Once the plastic is set, the ejection mechanism kicks in. It opens the mold to eject the finished product, then the cycle begins anew.
Materials Used in Injection Molding
Choosing the right materials for injection molding is key to creating quality products. The polymer selection process looks at several factors. These include resin properties and material compatibility, to fit the product needs.

Polymers are mainly used in injection molding. This includes thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers. Thermoplastics are popular for their flexibility. They melt when heated and solidify when cooled. This makes them great for recycling. Durable thermoplastics include:
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Thermosetting polymers, once set, can’t be melted again. They resist heat well and are strong. This makes them good for items needing to withstand high temperatures. Common types are:
- Epoxy Resins
- Phenolic Resins
- Melamine Formaldehyde
When we look at resin properties, we consider how they act under stress. For example, PE is chosen for being flexible and resisting water. PC is sought after for its toughness and clearness.
| Polymer | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Flexible, Moisture Resistant | Packaging, Containers |
| Polypropylene (PP) | High Chemical Resistance, Tough | Automotive Parts, Textiles |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | High Strength, Transparent | CDs, Eyewear Lenses |
Material compatibility is also key in choosing polymers. It’s important to pick materials that work well with others and the environment. This ensures the products last longer and perform better.
Common Applications of Injection Molding
Injection molding is a process used in many industries because it’s efficient, reliable, and cost-effective. It helps make automotive components and medical-grade plastics with precision. This technique is crucial in fields where quality and standards are top priorities. Let’s dive into some areas where injection molding is making a big difference.
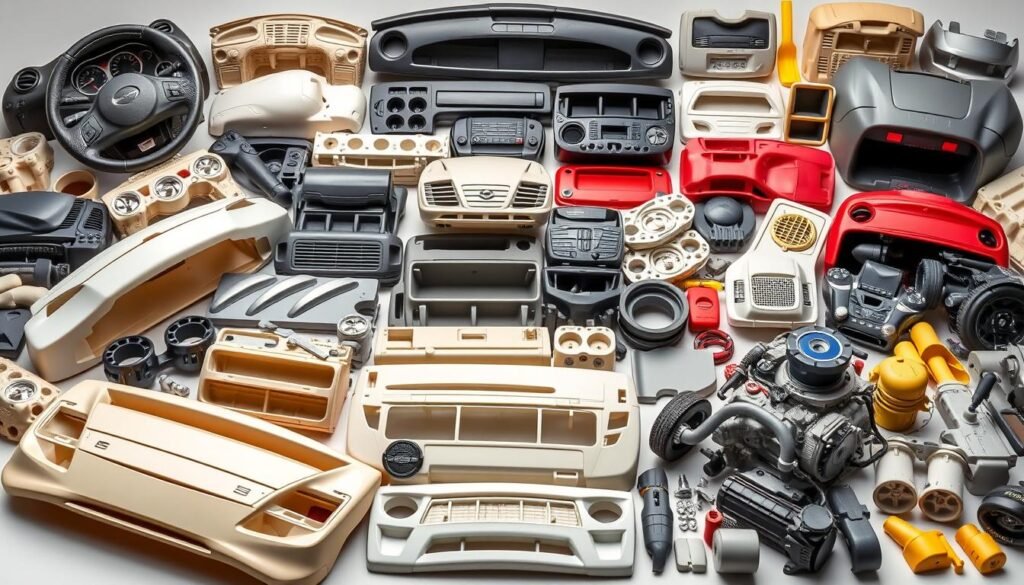
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector depends on injection molding for various parts. This method allows mass production of complex and sturdy automotive components. Items like dashboards, bumpers, and interior panels are made with consistency and top-notch quality. Thanks to precise tooling, injection molding meets the automotive industry’s strict requirements. For more on its benefits, see this detailed guide.

Consumer Goods
Injection molding is key in making consumer products. It’s used for items like toothbrushes, kitchen gadgets, and cases for electronics. The process lets manufacturers use different materials, creating various looks and feels. Injection molding is fast, wastes less material, and is good for the environment. Its adaptability and ease of use make it popular for making consumer goods.
Medical Devices
Manufacturing medical devices demands precision and cleanliness, making injection molding perfect. It’s used for syringes, surgical tools, and parts of diagnostic equipment. The technique ensures tight tolerances and minimal contamination of materials. Precision tooling helps meet strict specifications, ensuring devices are effective and safe.
Challenges and Solutions in Injection Molding
Injection molding can face many challenges that impact quality and speed. These include defects, inefficiencies, and issues with materials. To solve these problems, it’s key to understand them and find effective fixes.

To improve the process, optimizing molding parameters is vital. Adjusting temperatures, pressures, and cycle times can help. This makes parts mold better and reduce defects. It also cuts waste and saves money.
Quality control is crucial too. With advanced checks, we ensure parts meet standards. Methods like statistical process control (SPC) and monitoring catch errors early. This keeps quality consistent and reduces defects.
Troubleshooting in injection molding means finding the source of warping, sink marks, and fill issues. Analyzing the cycle and material flow helps solve these. Regular equipment upkeep and quality materials prevent many problems.
Here is a simple list of challenges and solutions:
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Defects in molded parts | Optimizing molding parameters and quality control measures |
| Inefficiencies in production | Regular maintenance and advanced monitoring techniques |
| Material complications | Using high-quality materials and proper storage conditions |
| Troubleshooting issues | Analyzing cycles, material flow and identifying root causes |
In summary, overcoming these issues with targeted solutions boosts production. By fine-tuning molding settings, ensuring quality control, and troubleshooting effectively, we make manufacturing more efficient and quality-driven.
Future Trends in Injection Molding Technology
Looking into the future, injection molding technology is about to change in big ways. A leading change is the growth of automation in manufacturing. With robots and better software, making things can become more precise. It means less waiting, fewer mistakes, and better products. This makes companies more competitive globally.
New and better materials are also changing the game. The creation of novel polymers and composites is fascinating. They are stronger, more bendable, and last longer. This lets us make more complex and efficient products. It’s really pushing injection molding to new heights.
Being green and eco-friendly is also more important now. This means using materials that are better for our planet. It also means using less energy and making less trash. Making products this way meets the demands of customers who want things that are kinder to Earth. It also follows stricter rules.
The mix of traditional molding and 3D printing integration is truly changing the industry. This combo means faster prototyping and making just what’s needed, when it’s needed. It allows for personalized products too. By combining these methods, manufacturers can make new, cost-efficient items.
The future of injection molding will be defined by its ability to adapt and integrate with these advanced technologies and sustainable practices, ensuring continuous improvement and innovation.
| Trend | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Automation in Manufacturing | Enhanced precision, reduced cycle times, minimized errors |
| Advanced Materials | Superior strength, flexibility, resistance |
| Eco-friendly Practices | Reduced waste, optimized energy, compliance with regulations |
| 3D Printing Integration | Rapid prototyping, on-demand production, customization |
Conclusion
As we sum up our journey, it’s clear that knowing injection molding is key to innovation and many job chances. We’ve covered the basics, how it works, and its big role in making things like cars, home goods, and medical tools. It’s important for anyone wanting to be great in this area to get this knowledge.
We’ve looked at how tricky injection molding can be, talked about ways to fix those issues, and looked at what’s next in technology. Keeping up with new information and changes is very important. This makes sure workers stand out and helps make making things faster and smarter.
Learning about injection molding combines knowing a lot and solving problems creatively. For those who want to get better in this area, there’s a lot of room to grow. As technology changes, so should our knowledge and skills. This helps us succeed and keep making progress in industry.
FAQ
What is injection molding?
Injection molding is a way to make many shapes and parts. It heats plastic and puts it into a mold. This method is popular for making lots of products quickly and cheaply.
What types of materials are used in injection molding?
Many materials like thermoplastics and polymers are used. The choice depends on the product’s needs. Factors like durability and flexibility are important.
What industries utilize injection molding?
Many industries use injection molding. For example, the auto industry for parts, consumer goods for everyday items, and the medical field for precise devices. It’s key for making varied products.
How does an injection molding machine work?
The machine heats plastic until soft. Then, it injects the plastic into a mold at high pressure. Once cool, you get the final product. Different parts of the machine are crucial for this.
What are the key components of the injection molding process?
Important parts include the injection unit, the mold system, and the clamping unit. The injection unit melts and injects the material. The mold shapes it. The clamping unit holds the mold closed. They all ensure a top-quality product.
What are common challenges in injection molding, and how can they be addressed?
Problems like warping and material issues happen. Fixing them involves adjusting how the molding is done, strict checking, and picking the right materials. Using new techniques and tech helps too.
What are future trends in injection molding technology?
The future looks at more automation and better materials. It focuses on being kinder to the environment and using 3D printing. The goal is to work more efficiently, lower harm to nature, and make better products.


