In today’s world, Precision CNC Turning is key for making top-notch parts. It lets us create parts that fit exact needs, making things more reliable and efficient. We’ll look into how CNC turning works, the machines used, and their benefits in many fields. For more on CNC precision machining, this article is a detailed guide on high-precision CNC turning.
Key Takeaways
- Precision CNC Turning is vital for producing rotational components.
- This process enables the achievement of high tolerances in manufacturing.
- Advanced machinery enhances the efficiency and quality of production.
- CNC precision machining is applicable across diverse industries.
- Understanding CNC turning mechanics improves product reliability.
- High-precision CNC turning contributes to cost-effective solutions.
What is CNC Turning?
CNC turning is a key process in making high-quality parts. It removes material from a rotating piece using special tools. This makes parts like cylinders and symmetrical shapes very accurately.
Understanding the Basics of CNC Turning
CNC lathe machining works by rotating a piece while tools cut into it. This makes parts quickly and to exact specifications. It’s used a lot in aerospace, cars, and medical fields.
It combines new tech with skilled work. This ensures parts are both precise and of high quality.
Difference Between CNC Turning and CNC Milling
CNC turning and CNC milling are different in how they work. CNC milling uses moving tools on a fixed piece. CNC turning uses fixed tools on a rotating piece.
This difference means CNC turning is better for making things like shafts and fittings. It’s very important for industries that need precision.
How CNC Turning Works
The CNC turning process is very detailed. It involves many steps to make high-quality parts. This method uses advanced technology and follows a set of rules for making parts.
The CNC Turning Process Explained
First, we use a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) model to plan the part’s shape. Then, we turn this design into G-code with Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software. This code tells the machine how to move and cut the part.
This careful planning helps CNC turning makers make parts accurately and the same every time.
Key Steps in CNC Turning Operations
- Machine Setup: We place the workpiece on the lathe and make sure it’s aligned right for cutting.
- Turning Process: We start the workpiece spinning and use the cutting tool to shape it as planned.
- Inspection: We check the finished part carefully to make sure it meets high standards.
This method makes sure the parts are not only made fast but also reliable. It’s a key part of modern making things.
Types of CNC Turning Machines

CNC turning uses many machines for different needs. Each machine has its own benefits. Knowing these types helps pick the right CNC turning center for your project.
Horizontal Lathes
Horizontal lathes are common in machining. They are versatile and make many cylindrical parts well. They are great for making parts with tight tolerances.
Vertical Lathes
Vertical lathes are good for big parts. They have better stability and weight distribution. This makes machining more accurate for large parts.
Swiss-Type Lathes and Multi-Axis Turning Centers
Swiss-type lathes make small parts with tight tolerances. They are used a lot in medical device making. Multi-axis turning centers can make complex shapes from many angles. This makes them very efficient and accurate.
To learn more about CNC machines and their uses, check out this resource.
Advantages of Precision CNC Turning

Precision CNC turning is great for making high-quality parts. It can create precision turned parts with complex designs. This means the parts are strong and meet industry standards.
High Precision and Consistency
CNC turning is known for its high precision. It can make parts with very tight tolerances. This means every part is made exactly right, without needing extra work.
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
CNC turning saves money by using less labor and material. It works well for making lots of parts or just a few. This makes it flexible for different projects. For more details, check out our CNC machining services.
Applications of CNC Turning in Various Industries

CNC turning is key in many important fields. It makes high-quality parts for industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. This shows how versatile and precise CNC turning is.
Aerospace and Automotive Applications
In aerospace, CNC turning makes parts like turbine shafts and landing gear. These parts need to be very precise and meet strict standards. This ensures safety and performance.
In the automotive world, CNC turning makes drive shafts and gears. These parts need to be reliable and last long.
Medical Device Manufacturing
The medical field uses CNC turning for surgical tools and implants. These parts must be very precise because they are close to patients. CNC turning helps make devices that are both precise and strong, improving patient care.
Electronics and Oil & Gas Sectors
In electronics, CNC turning makes small parts for devices. This lets makers create detailed designs that fit tight spaces. The oil and gas industry uses CNC turning for strong valve parts and fittings. These parts need to handle tough conditions.
| Industry | Components Produced | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine shafts, bushings | High precision, strict standards |
| Automotive | Drive shafts, gears | Durability, reliability |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments, implants | Exact specifications, performance |
| Electronics | Small components | Tight tolerances, intricate designs |
| Oil & Gas | Durable valve components | Resistance to harsh conditions |
Precision CNC Turning: Achieving High-Quality Standards
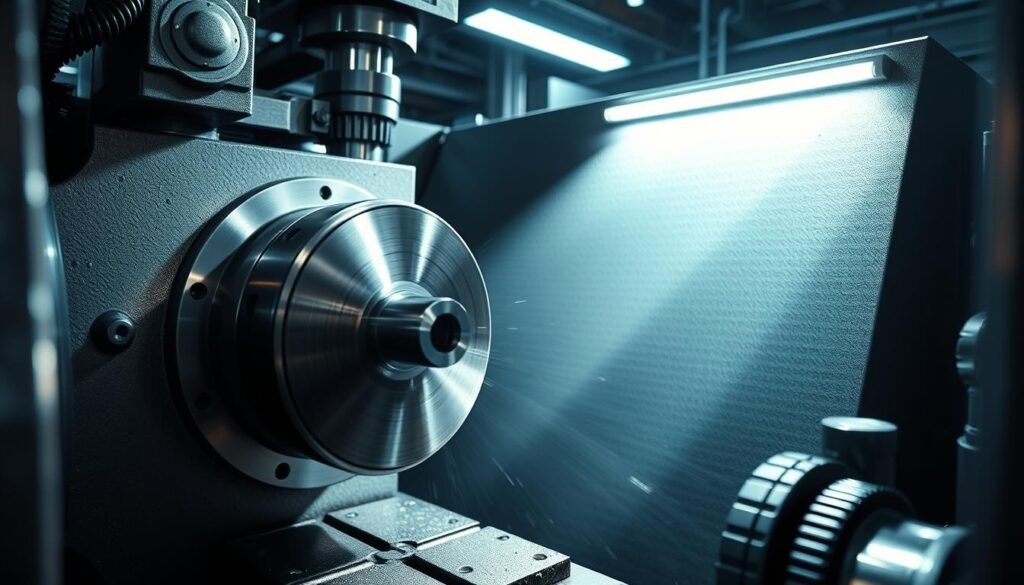
High-quality standards in CNC turning depend on strict tolerances. These tolerances make sure parts work right and are safe. They meet needs in many fields.
Importance of Tolerances in CNC Turning
Tight tolerances, like 0.00004 inches, are key in CNC machining. Aerospace and medical fields need perfect accuracy. Even small mistakes can be very bad.
By keeping these tight tolerances, makers create parts that work well and are safe.
Meeting Industry Specifications and Standards
Each industry has its own rules. Following these rules is crucial for good work. Our goal is to meet industry standards with careful quality checks.
We check parts at different stages to make sure they’re up to par. Using advanced CAD/CAM tech helps us make precise plans for machining. This makes our CNC turning a trusted choice for important jobs.
Materials Used in CNC Turning
CNC turning works with many materials. This makes it great for lots of industries. It can make parts that fit special needs.
Common Metals and Their Applications
When it comes to CNC turning metals, some stand out. They have special qualities:
- Stainless Steel: Grades like 304, 316, and 17-4 PH are great for fighting corrosion and lasting long.
- Aluminum: 6061-T6 is light and easy to work with.
- Titanium Alloys: They are strong and light, perfect for space.
- Copper Alloys: 101 and 110 are good for handling heat and electricity.
- Brass: 360 brass is easy to work with and doesn’t rust much.
Plastics and Composites in CNC Turning
CNC turning also works with CNC turning plastics. These plastics are key in many fields. Here are some examples:
- Nylon: It’s tough and used in machines.
- PEEK: It’s great for chemicals and high heat, used in medical stuff.
- Polycarbonate: It’s strong and used in electronics.
- HDPE: It’s light and strong, used in many places.
Choosing the right materials for CNC turning is key. It affects how well parts work and last. Using the right materials ensures parts are top-notch and meet high standards.
| Material Type | Property | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistant | Medical and aerospace components |
| Aluminum | Lightweight and strong | Automotive and structural applications |
| Titanium Alloys | High strength-to-weight ratio | Aerospace and military applications |
| Copper Alloys | High conductivity | Electrical connectors |
| Brass | Excellent machinability | Plumbing fixtures |
| Nylon | Durable and abrasion resistant | Mechanical parts |
| PEEK | High chemical resistance | Medical devices |
Challenges and Trends in CNC Turning
CNC turning faces many challenges for manufacturers to keep quality high. Tool wear and material limits are big issues. They affect how well things are made and how efficient the process is. Knowing these problems helps businesses improve their machining.
Dealing with Tool Wear and Material Limitations
Tool wear is a big problem in CNC turning. Tools get worn out from all the work. Keeping tools in good shape is key.
Choosing the right materials is also important. Harder materials need stronger tools. This can make things more expensive.
Emerging Technologies in Precision Engineering
New technologies are changing CNC turning. Automation and real-time monitoring make things better. Automation means less human error and more precision.
Real-time monitoring helps spot tool problems fast. This means tools can be fixed before they get too bad.
| Technology | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Automation | Integration of robotics and automated systems in machining processes. | Increased efficiency, reduced labor costs. |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Continuous tracking of tool performance and condition. | Immediate diagnostics, better maintenance scheduling. |
| Hybrid Machining | Combines different machining processes, such as CNC turning with additive manufacturing. | Greater flexibility, enhanced capabilities. |
| Sustainable Practices | Utilization of eco-friendly materials and processes. | Reduced environmental impact, compliance with regulations. |
Conclusion
Precision CNC turning is key in the manufacturing world. It offers high-precision solutions that make top-quality parts. This is vital in many fields like aerospace, cars, and medical devices.
CNC turning brings many benefits. It makes things more efficient and cheaper. This makes it a mainstay in today’s factories.
We keep improving our CNC turning skills. This puts us at the top of precision engineering. We stay ahead by using new tech and meeting industry needs.
We promise to keep making parts of the highest quality. This commitment helps businesses that need precise CNC turning. We aim to always meet their needs.
FAQ
What is precision CNC turning?
Precision CNC turning is a way to make parts by cutting away material. It uses tools to remove material from a spinning piece. This method ensures parts are made exactly right.
What industries benefit from CNC turning services?
Many industries use CNC turning. These include aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. It’s also used in electronics and oil & gas. It helps make parts that meet very high standards.
How does CNC turning differ from CNC milling?
CNC turning and milling work differently. Turning uses a spinning piece and stationary tools. Milling uses tools that move and a stationary piece.
What types of machines are used in CNC turning?
CNC turning uses many machines. There are horizontal and vertical lathes. Also, Swiss-type lathes for detailed parts and multi-axis centers for complex shapes.
What advantages does precision CNC turning offer?
CNC turning has many benefits. It’s precise and consistent. It’s also cost-effective and can handle both small and large orders.
How do you ensure high-quality standards in CNC turning?
We follow strict rules for quality. We check parts carefully and watch the process closely. This makes sure parts meet all standards.
What materials can be used in CNC lathe machining?
CNC lathes work with many materials. This includes metals like aluminum and stainless steel. It also works with plastics and composites, great for medical and aerospace.
What are some challenges in CNC turning?
CNC turning faces some challenges. These include tool wear and material limits. But, new tech like automation helps solve these problems.
How does CNC precision machining enhance production efficiency?
CNC machining makes production better. It automates tasks and cuts down on mistakes. It also uses materials wisely and makes adjustments as needed.


